Research Note
Using More Distillers? Watch PUFA & DCAD
Corn distillers grains with solubles (DDGS or “distillers”) provides a cost-effective protein, fiber, and fat source in dairy rations, especially during high-supply-reduced-export conditions.
But optimizing distillers use requires close attention to polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). In addition, new studies emphasize dietary cation-anion difference (DCAD) in maintaining lactation performance and avoiding milk fat depression (MFD).
“More than a decade of research pointed up the possible negative effects on milk fat from high levels of PUFA in ‘traditional’ or conventional DDGS,” says Dr. Chanhee Lee of the Ohio State University. “The advent of reduced-fat DDGS has helped increase applications in lactation rations.”
Traditional DDGS has a total fatty acid (FA) content around 11.5% versus 8.0% for reduced-fat DDGS, while some sources may offer even lower FA concentrations.
“However,” Lee adds, “feeding a high reduced-fat DDGS diet (>20% on a DM basis) still can result in negative production, especially affecting milk fat.”
For example, an Ohio State study fed reduced-fat DDGS at 29% (DM basis) continuously for 11 weeks and found lower milk fat yield and energy-corrected milk. These effects became more severe as the experiment progressed, reaching a 35% decline in milk fat yield.
“We speculated that PUFA — even in reduced-fat DDGS — may not be the only factor contributing to milk fat depression.”
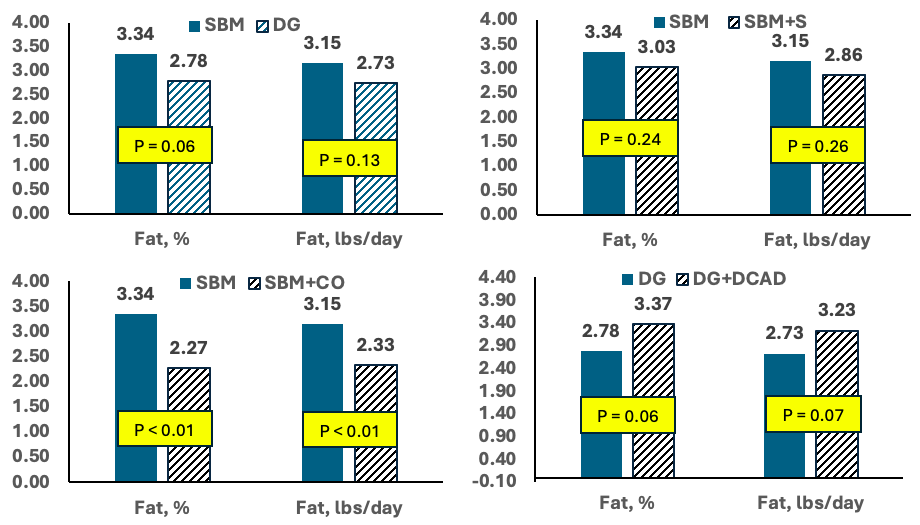
It turns out that sulfur (S) concentration in DDGS is relatively high compared to SBM and increases S concentration about 0.2% (DM basis) when fully replacing SBM and soyhulls. Lee points out that above 0.15-0.25% in lactation diets (NASEM, 2021), S can reduce rumen fermentation and fiber digestibility. It also can act as a trace mineral antagonist. Those are “direct” effects.
“Indirectly,” Lee says, “excess sulfur decreases DCAD.
“So diets containing 20-30% DDGS on a dry matter basis can reduce DCAD to less than 100 mEq/kg DM. Typically, DCAD is around 200 mEq/kg DM for lactating cow diets without additional cation supplementation.”
Recent work has confirmed that MFD occurs with inclusion of reduced-fat DDGS at 30% (DM basis), partly as a result of high PUFA. Yet the high S content of DDGS also contributed to MFD by reducing DCAD.
Milk fat concentration and yield of cows fed the SBM, DG (DDGS), SBM+S, SBM+CO (corn oil), or DG+DCAD diet (adapted from Clark et al., 2024).
“In this study, increasing DCAD eliminated MFD in the DDGS diet,” Lee points out. “So, in DDGS diets over 20% on a dry matter basis, we suggest increasing DCAD to around 300 mEq/kg DM.
“Keep in mind that distillers is a co-product of corn ethanol processing. Amino acid, fatty acid, and mineral contents can vary depending on supplier and other factors.”
Questions?
Email FeedInsight 4Dairy