Summer DCAD: The K Source Option
Summer DCAD: The K Source Option
Thanks to many advances in dairy production, maintaining rumen balance year-round is not as big a problem as it used to be, notes Clemson Emeritus Professor Tom Jenkins.
Yet summer still impacts rumen balance and milk components due to changes in forages, the mix of other macro ingredients, feeding regimen and other management factors. On top of it all, there’s heat stress with hot, humid weather day and night.
There’s a high correlation between rumen imbalance and summer milk fat decline.
Keeping rumen balance
We want to sustain rumen balance to prevent rumen microorganisms from over-producing trans fatty acids, particularly CLA (conjugated linoleic acids), which can inhibit mammary (de novo) milk fat synthesis. How?
Our formulation toolbox includes ways to adjust DCAD (dietary cation anion difference) according to stage of lactation. DCAD can affect rumen pH, where we want lower DCAD prepartum and higher DCAD postpartum, which results in higher pH to help sustain rumen balance during lactation.
The charge balance of the major cations (K and Na) and anions (Cl and S) determines the diet’s DCAD.
So potassium (K) plays a key role maintaining the blood acid-base balance through DCAD while supporting many other vital functions. We especially want to avoid negative K balance during lactation.
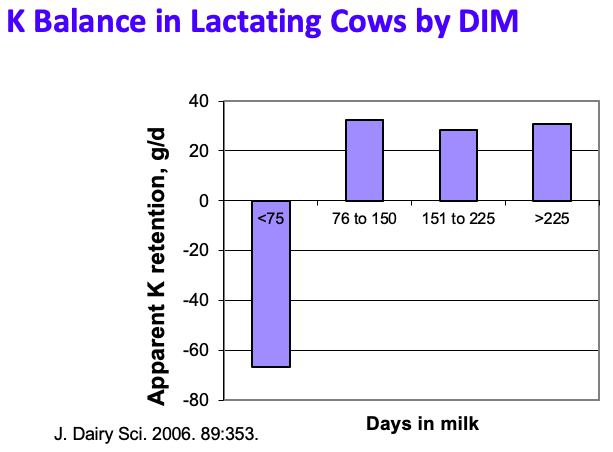
Cows lose K naturally through the milk but there is a particular risk during heat stress when they also lose it through sweat. Negative K balance can upset milk synthesis and affect concentration of milk components, including milk fat.
Tweaking buffer mix
The most popular rumen buffer, sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), increases DCAD through the sodium cation. However, raising DCAD through the K cation also supports the cow’s K balance.
A couple K sources can have a positive effect on milk fat.
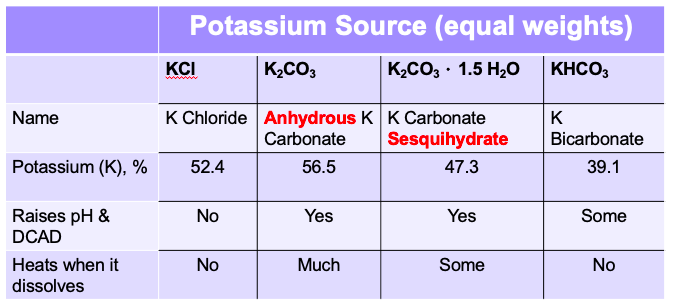
So while bicarb may be your go-to buffer, potassium carbonate sesquihydrate (K2CO3 – 1.5 H2O) offers good pH and DCAD increase along with K balancing potential.
This K source is more expensive but may be worth working into the buffer mix to help mitigate summer milk fat loss.
Questions?
Email FeedInsight 4Dairy

