Reactivity of Minerals For Dairy Cattle Estimated Through The “White Vinegar Test”

REACTIVITY OF MINERALS FOR DAIRY CATTLE ESTIMATED THROUGH THE “WHITE VINEGAR TEST”
UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH RIDGETOWN CAMPUS
Presented by: Dr. Gail Carpenter
Prepared for: The National Lime & Stone Company
Date: September 15, 2017
Introduction
A variety of calcium and magnesium supplements for dairy cattle exist on the market today; however, the efficacy of these supplements depends on their bioavailability, which is in part impacted by the reactivity and alkalizing properties of these supplements. In the experiments described here, we estimated the relative reactivity of commercially available supplements using the white vinegar test (WVT) proposed by Goff (2014).
Methods
Two experiments were performed to determine the alkalizing properties of the test minerals through the WVT (Goff, 2014). In brief, 3 g of each supplement was weighed into a 50-mL centrifuge tube, and 40 mL of 5% acetic acid was added. Tubes were capped and shaken for 15 sec. After 15 min., the tubes were shaken again and left to sit for 15 more min., at which time, pH was measured and recorded. A higher 30-min pH is considered indicative of more reactivity and presumably more bioavailability.
In the first experiment, the mineral supplements were tested individually. These supplements were Product Y, Product X, NatMag99, and NatMag99 Fine. Product X, Product Y, and the NLS grades are magnesium limestone products. In the second experiment, NLS products were sampled from the packaging plant and compared to Product Y and Product X. Packaging plant samples are finer than bulk material of the same grade due to extra handling. For this experiment, we again compared Product X, Product Y, NatMag99, and NatMag99 Fine.
Data was analyzed using PROC GLM of SAS (version 9.4). Significance was declared at P < 0.01.
Results
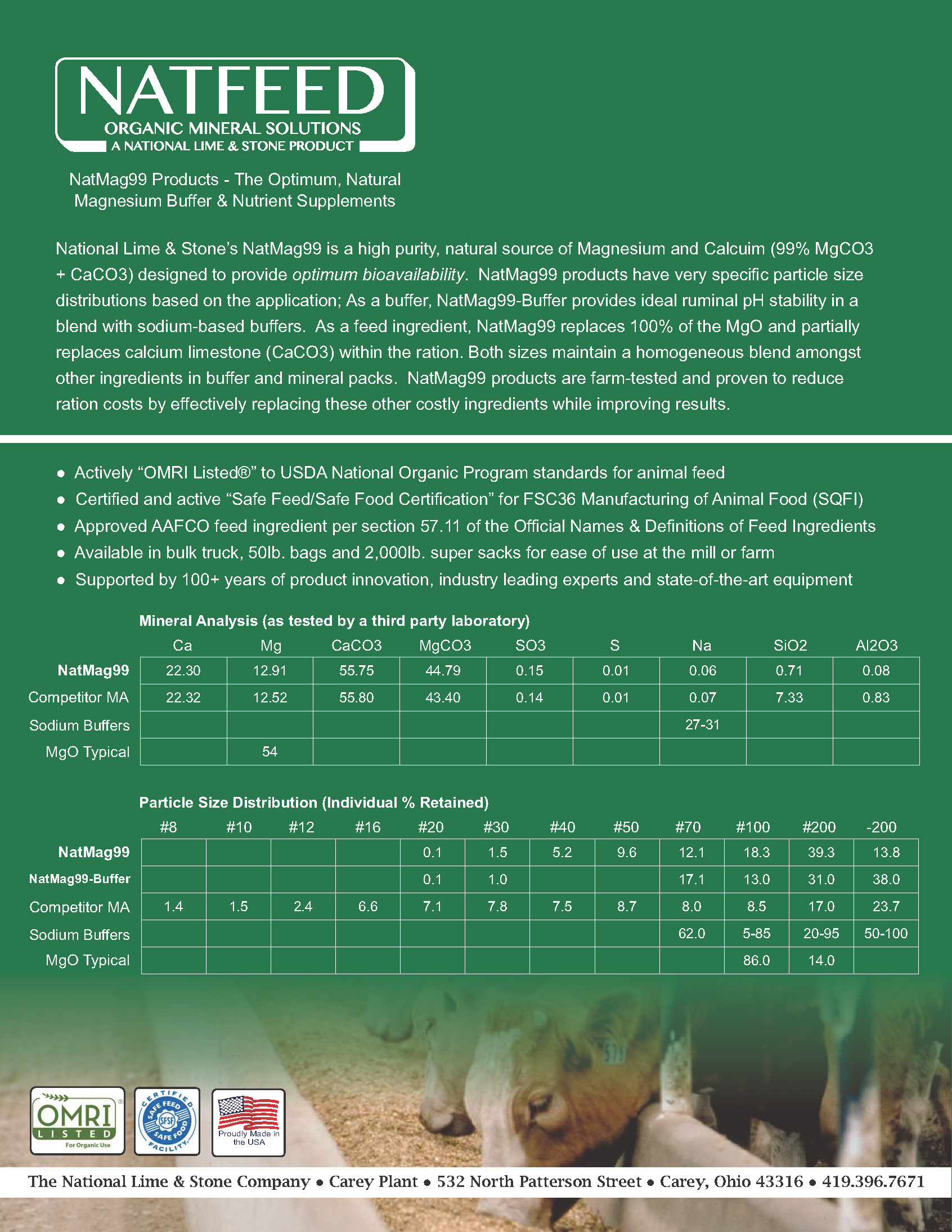
Results for Experiment 1 are presented in Figure 1. Because of the very low standard error of the results (SE = 0.009), it is difficult to determine whether the results presented here have physiological significance. All supplements had a 30-min pH between 3.53 and 3.76.
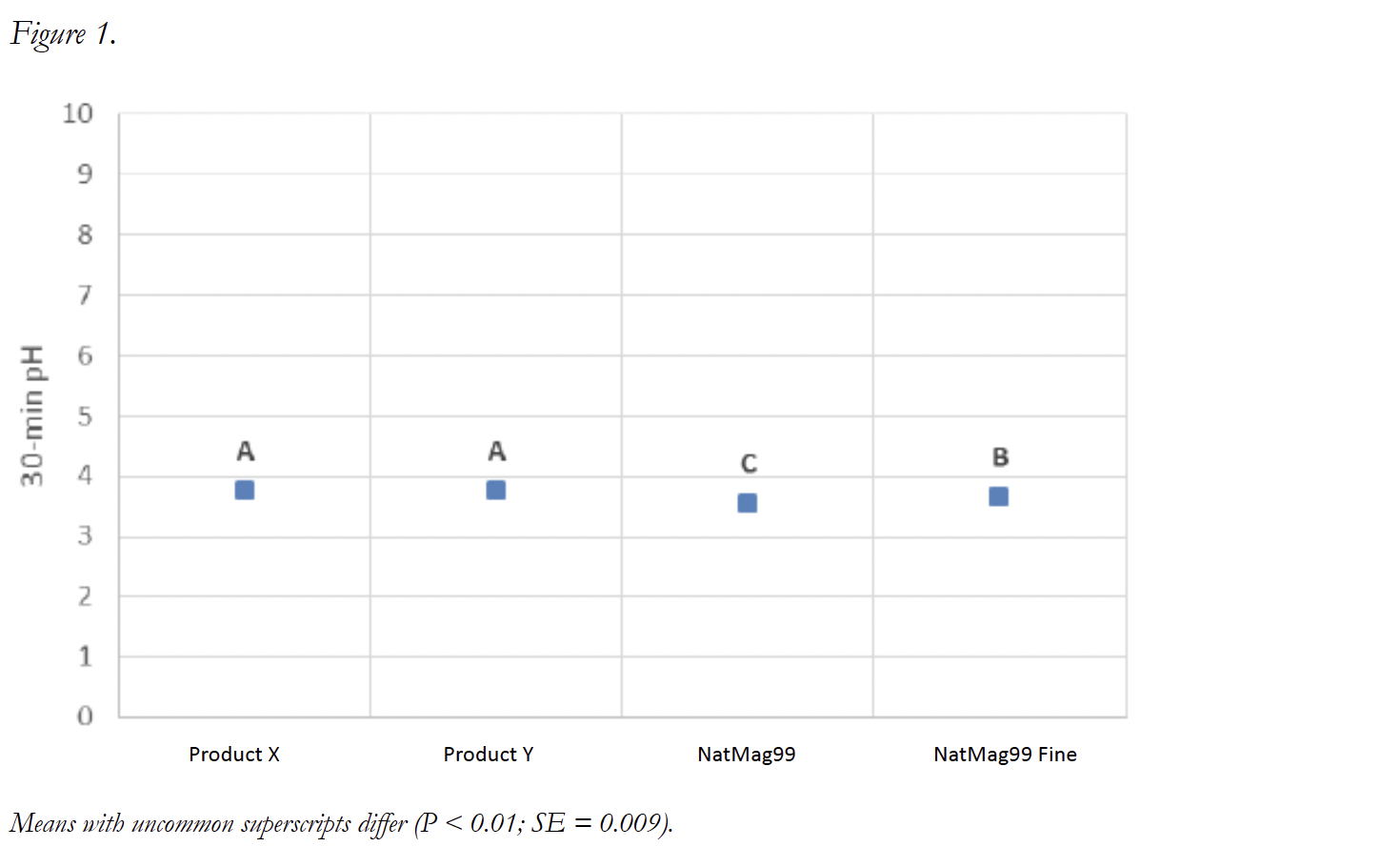
Results for Experiment 2 are presented in Figure 2. 30-min pH ranged from 3.48 (NatMag99) to 3.62 (Product Y), so again, the physiological implications of this experiment are difficult to determine because of the low variation in the results (SE = 0.018).
Implications
In the results described here, it is reasonable to conclude that statistical differences between magnesium limestone supplements are due to the low variation associated with the technique, andthese experiments indicate that NatMag99 and NatMag99 Fine are similar to Product Y and Product X in the analyses performed. While statistical differences were detected using the WVT between various magnesium limestone supplements, to determine whether or not these differences are physiologically significant would require further experiments in live animals.
Reference
Goff, J.P. 2014. Calcium and magnesium disorders. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 30:359 – 381.